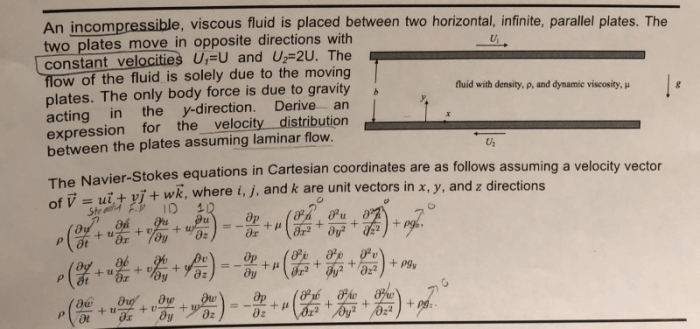
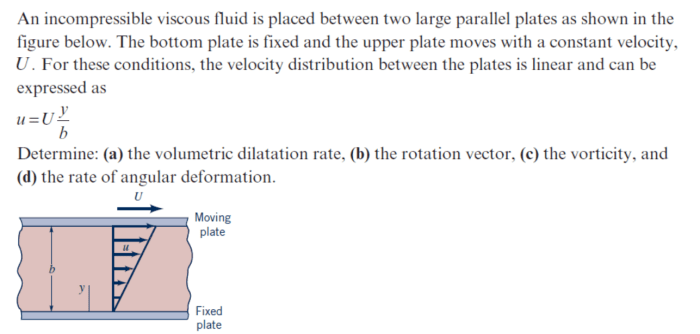
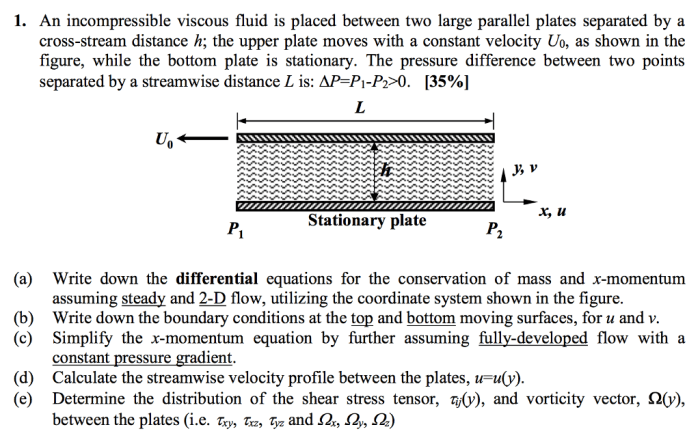
An incompressible viscous fluid is placed at the forefront of this discourse, inviting us to delve into its captivating realm. These fluids, characterized by their inability to be compressed and their inherent resistance to flow, exhibit unique properties and play pivotal roles in diverse real-world applications.
Their presence in everyday life is undeniable, from the smooth flow of honey to the intricate workings of hydraulic systems. Understanding the behavior and dynamics of incompressible viscous fluids is paramount in various fields, including engineering, physics, and medicine.
Introduction: An Incompressible Viscous Fluid Is Placed
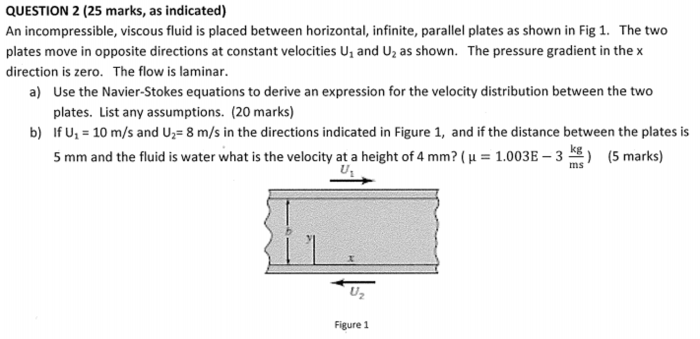
An incompressible viscous fluid is a substance that does not change its volume under pressure and exhibits resistance to flow due to its internal friction. These fluids are characterized by their inability to be compressed and their ability to resist deformation.
Incompressible viscous fluids are commonly encountered in various industrial and scientific applications, such as hydraulic systems, lubrication, and fluid mechanics studies.
Applications
- Hydraulic systems:Incompressible viscous fluids are used in hydraulic systems to transmit power and motion. They are preferred due to their ability to withstand high pressures and their resistance to cavitation.
- Lubrication:Incompressible viscous fluids are used as lubricants to reduce friction between moving surfaces. They form a thin film between the surfaces, preventing direct contact and reducing wear.
- Fluid mechanics studies:Incompressible viscous fluids are used as model fluids in fluid mechanics studies. They provide insights into the behavior of more complex fluids and allow researchers to develop theoretical models and computational tools.
Flow Dynamics
The flow behavior of incompressible viscous fluids is governed by fundamental principles, including conservation of mass, momentum, and energy.
Key factors influencing fluid flow include:
- Pressure:Pressure gradients drive fluid flow from regions of high pressure to low pressure.
- Velocity:Velocity is the rate at which fluid particles move. Velocity gradients within the fluid create shear stresses.
- Viscosity:Viscosity is a measure of the fluid’s resistance to flow. Higher viscosity fluids exhibit greater resistance to deformation.
Fluid Mechanics Equations, An incompressible viscous fluid is placed
The governing equations for incompressible viscous fluid flow are known as the Navier-Stokes equations. These equations are a set of partial differential equations that describe the conservation of mass, momentum, and energy.
Each term in the Navier-Stokes equations has a specific physical significance:
- Convection term:Describes the transport of fluid properties due to fluid motion.
- Diffusion term:Describes the spread of fluid properties due to molecular motion.
- Pressure term:Represents the forces due to pressure gradients.
- Viscous term:Represents the forces due to viscous stresses.
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD)
CFD is a powerful tool for analyzing and simulating the behavior of incompressible viscous fluids. It involves solving the Navier-Stokes equations numerically to predict fluid flow and other relevant parameters.
CFD techniques include:
- Finite element method (FEM):Divides the fluid domain into small elements and solves the equations within each element.
- Finite volume method (FVM):Divides the fluid domain into small control volumes and solves the equations for each volume.
- Smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH):Represents the fluid as a collection of particles and solves the equations for each particle.
Experimental Techniques
Experimental techniques are used to study the behavior of incompressible viscous fluids in real-world scenarios.
Common experimental methods include:
- Flow visualization:Uses techniques such as dye injection or particle tracking to visualize fluid flow patterns.
- Pressure measurement:Uses pressure sensors to measure pressure at different locations within the fluid.
- Velocity measurement:Uses techniques such as laser Doppler velocimetry (LDV) or particle image velocimetry (PIV) to measure fluid velocity.
Answers to Common Questions
What is an incompressible viscous fluid?
An incompressible viscous fluid is a fluid that cannot be compressed and exhibits resistance to flow due to its internal friction.
What are some examples of incompressible viscous fluids?
Honey, oil, and water are common examples of incompressible viscous fluids.
What are the key properties of incompressible viscous fluids?
Incompressibility, viscosity, and density are the key properties of incompressible viscous fluids.