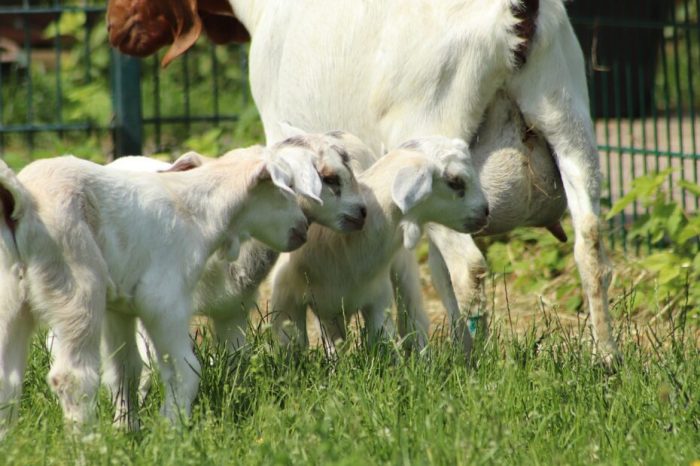
First freshener goat udder development is a critical aspect of dairy goat production, influencing milk yield, udder health, and overall profitability. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the anatomical, physiological, and management factors that impact udder development in first-fresheners.
Understanding the complexities of udder development is essential for goat producers to optimize milk production and ensure the well-being of their animals.
Anatomy and Physiology of Goat Udder Development: First Freshener Goat Udder Development

The goat udder is a mammary gland responsible for producing and secreting milk. It consists of two symmetrical halves, each with a teat. The udder is composed of glandular tissue, connective tissue, and blood vessels.
During the first freshening, the udder undergoes significant development under the influence of hormones, primarily prolactin and oxytocin. Prolactin stimulates the growth and development of the glandular tissue, while oxytocin triggers milk ejection during milking.
Factors Influencing Udder Development
Several factors influence the size and shape of the udder in first-fresheners:
- Breed:Different goat breeds have varying udder characteristics, such as size, shape, and teat placement.
- Genetics:The genetic makeup of an individual goat can influence udder development and milk production potential.
- Nutrition:Adequate nutrition, particularly during pregnancy and lactation, is crucial for optimal udder development and milk production.
- Environmental factors:Temperature, stress, and other environmental conditions can affect udder development and milk yield.
Stages of Udder Development
Udder development in first-fresheners typically occurs in distinct stages:
- Pre-pubertal stage:The udder is small and underdeveloped.
- Pubertal stage:The udder begins to enlarge and develop rudimentary teats.
- Pregnancy stage:The udder undergoes significant growth and development, preparing for milk production.
- Lactation stage:The udder reaches its full development and produces milk.
Udder Health and Management
Maintaining udder health is essential for optimal milk production and goat welfare:
- Mastitis:An infection of the mammary gland that can lead to decreased milk production and quality.
- Edema:Swelling of the udder due to fluid retention, which can interfere with milking and milk production.
Best practices for udder health include proper milking techniques, udder hygiene, and preventive measures such as vaccination.
Milk Production and Udder Capacity
The size and development of the udder are indicative of the milk production potential of a first-fresher:
- Larger udders:Typically associated with higher milk production.
- Well-developed udders:Exhibit good texture, elasticity, and teat placement.
Factors such as genetics, nutrition, and management practices influence milk yield and udder capacity.
Case Studies and Examples, First freshener goat udder development
Successful first-fresheners with well-developed udders showcase the positive impact of proper management practices:
Example:A first-freshening goat with a well-developed udder and high milk production was raised on a farm that emphasized optimal nutrition, regular milking, and preventive healthcare.
Helpful Answers
What are the key stages of udder development in first-fresheners?
The stages of udder development include pre-pubertal, pubertal, pre-lactational, lactational, and post-lactational.
How does nutrition influence udder development?
Proper nutrition, particularly during the pre-pubertal and pre-lactational periods, is crucial for optimal udder growth and development.
What are common udder health issues in first-fresheners?
Mastitis and edema are common udder health issues that can affect first-fresheners.