Nitric acid, a compound renowned for its corrosive nature and diverse applications, presents a compelling question: is nitric acid heterogeneous or homogeneous? Delving into the intricacies of its composition and properties, this exploration unravels the enigmatic nature of nitric acid, revealing its true identity.
Nitric acid, a colorless liquid with a pungent odor, holds a prominent position in the chemical industry. Its versatility extends to a wide range of applications, including the production of fertilizers, explosives, and dyes. Understanding the homogeneity or heterogeneity of nitric acid is crucial for comprehending its behavior and optimizing its use in various domains.
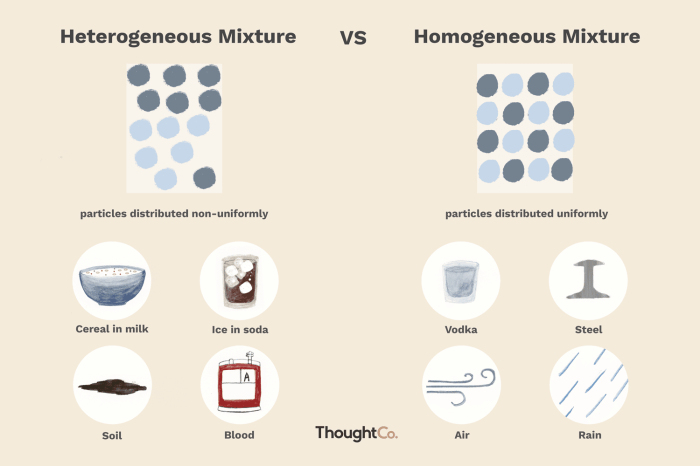
Definition of Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Mixtures: Is Nitric Acid Heterogeneous Or Homogeneous

A homogeneous mixture is a mixture in which the components are evenly distributed throughout the mixture, resulting in a uniform composition. In contrast, a heterogeneous mixture is a mixture in which the components are not evenly distributed, resulting in a non-uniform composition.
Examples of homogeneous mixtures include saltwater, air, and milk. Examples of heterogeneous mixtures include sand in water, oil in water, and salad.
Composition and Properties of Nitric Acid
Nitric acid is a highly corrosive, toxic, and colorless liquid with the chemical formula HNO 3. It is composed of hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen atoms.
Nitric acid has several important physical and chemical properties, including:
- Density: 1.51 g/mL
- Boiling point: 83 °C
- Melting point: -42 °C
- Highly reactive
- Strong oxidizing agent
Heterogeneity and Homogeneity of Nitric Acid

Nitric acid is considered a homogeneous mixture because it is composed of only one substance: HNO 3. The molecules of HNO 3are evenly distributed throughout the solution, resulting in a uniform composition.
Evidence supporting the classification of nitric acid as a homogeneous mixture includes:
- The solution has a uniform appearance and color.
- The solution has a constant density and boiling point.
- The solution does not separate into different layers over time.
Factors Affecting Homogeneity
The homogeneity of nitric acid can be affected by several factors, including:
- Temperature:Changes in temperature can affect the solubility of the components in the mixture, leading to changes in homogeneity.
- Pressure:Changes in pressure can also affect the solubility of the components in the mixture, leading to changes in homogeneity.
- Concentration:The concentration of the components in the mixture can affect the homogeneity of the mixture. For example, a mixture of concentrated nitric acid and water may not be homogeneous due to the different solubilities of the two components.
Applications of Nitric Acid

Nitric acid is used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Fertilizer production:Nitric acid is used to produce ammonium nitrate, which is a common fertilizer.
- Explosive production:Nitric acid is used to produce explosives such as dynamite and nitroglycerin.
- Metalworking:Nitric acid is used to etch and clean metals.
- Chemical synthesis:Nitric acid is used to produce a variety of chemicals, including dyes, pharmaceuticals, and plastics.
The homogeneous nature of nitric acid contributes to its usefulness in these applications. The uniform composition of nitric acid ensures that it reacts consistently and predictably, which is essential for many industrial processes.
Q&A
Q: What is the chemical formula of nitric acid?
A: HNO3
Q: Is nitric acid a strong or weak acid?
A: Strong acid
Q: What is the pH of nitric acid?
A:< 1


