Most TP sensors have how many wires? This intriguing question unveils a complex tapestry of wire configurations in temperature sensors, each designed to fulfill specific applications with varying degrees of accuracy and efficiency. Delve into this comprehensive guide to unravel the mysteries of TP sensor wiring, empowering you with the knowledge to navigate the intricacies of temperature measurement.
From the fundamental principles of temperature sensing to industry-standard wiring practices, this discourse explores the nuances of TP sensor wire configurations, empowering you to make informed decisions for your temperature measurement needs.
Types of Temperature Sensors

Temperature sensors are devices that measure the temperature of a system or environment. They are used in a wide range of applications, from industrial processes to consumer electronics. There are many different types of temperature sensors, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
The most common type of temperature sensor is the thermocouple. Thermocouples are made of two dissimilar metals that are joined together at one end. When the junction is heated, a voltage is generated that is proportional to the temperature difference between the junction and the other end of the thermocouple.
Thermocouples are relatively inexpensive and can be used to measure a wide range of temperatures. However, they are not very accurate and can be affected by electrical noise.
Another common type of temperature sensor is the resistance temperature detector (RTD). RTDs are made of a metal that has a known resistance at a specific temperature. When the temperature of the RTD changes, its resistance also changes. RTDs are more accurate than thermocouples and are not affected by electrical noise.
However, they are more expensive than thermocouples and can only be used to measure a limited range of temperatures.
Semiconductor temperature sensors are also commonly used. These sensors are made of a semiconductor material that has a resistance that is dependent on temperature. Semiconductor temperature sensors are accurate and can be used to measure a wide range of temperatures.
However, they are more expensive than thermocouples and RTDs.
Infrared temperature sensors measure the temperature of an object by detecting the infrared radiation that it emits. Infrared temperature sensors are non-contact, which means that they can be used to measure the temperature of objects that are difficult to reach or that are moving.
However, infrared temperature sensors are not as accurate as thermocouples, RTDs, or semiconductor temperature sensors.
Wire Configurations of Temperature Sensors

Temperature sensors can have different wire configurations. The most common wire configurations are 2-wire, 3-wire, and 4-wire configurations.
2-wire temperature sensors have two wires: a signal wire and a ground wire. The signal wire carries the electrical signal that is generated by the sensor. The ground wire provides a reference point for the electrical signal.
3-wire temperature sensors have three wires: a signal wire, a ground wire, and a shield wire. The shield wire helps to protect the signal wire from electrical noise.
4-wire temperature sensors have four wires: a signal wire, a ground wire, a shield wire, and an excitation wire. The excitation wire provides a voltage reference for the sensor.
Industry Standards for Temperature Sensor Wiring: Most Tp Sensors Have How Many Wires
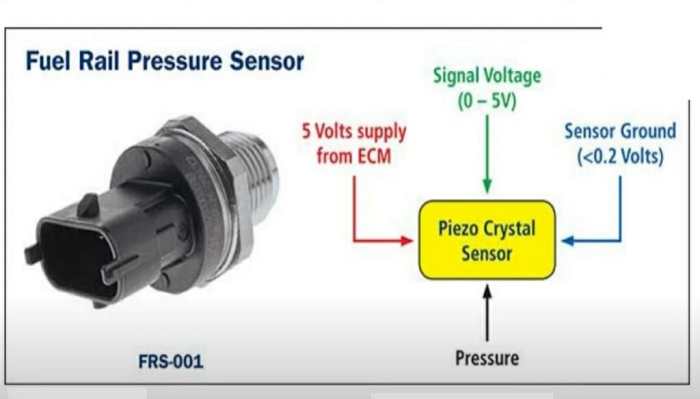
There are several industry standards that govern the wiring of temperature sensors. These standards ensure that temperature sensors are wired correctly and safely.
One of the most common industry standards for temperature sensor wiring is the National Electrical Code (NEC). The NEC is a set of regulations that govern the electrical wiring of buildings and other structures. The NEC includes requirements for the wiring of temperature sensors, including the type of wire that can be used, the size of the wire, and the way that the wire is installed.
Another common industry standard for temperature sensor wiring is the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standard 60584-2. This standard provides guidelines for the design, installation, and testing of temperature sensors. The IEC 60584-2 standard includes requirements for the wiring of temperature sensors, including the type of wire that can be used, the size of the wire, and the way that the wire is installed.
Troubleshooting Wiring Issues in Temperature Sensors

There are several common wiring issues that can occur in temperature sensors. These issues can cause the sensor to malfunction or to provide inaccurate readings.
One of the most common wiring issues is a loose connection. A loose connection can occur anywhere in the wiring, from the sensor to the controller. Loose connections can cause the sensor to malfunction or to provide intermittent readings.
Another common wiring issue is a short circuit. A short circuit occurs when two wires come into contact with each other. Short circuits can cause the sensor to malfunction or to provide inaccurate readings.
A third common wiring issue is an open circuit. An open circuit occurs when a wire is broken or disconnected. Open circuits can cause the sensor to malfunction or to provide no readings at all.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the most common wire configuration for TP sensors?
The most common wire configuration for TP sensors is the 2-wire configuration, which utilizes a single pair of wires for both power and signal transmission.
What is the advantage of using a 3-wire TP sensor?
3-wire TP sensors offer increased accuracy compared to 2-wire sensors due to the dedicated wire for signal transmission, which eliminates the impact of voltage drop on the signal.
What industry standards govern TP sensor wiring?
TP sensor wiring is governed by industry standards such as IEC 60584-2 and ANSI/ISA-50.00.01, which specify wire colors, terminal designations, and other wiring practices.